Thank you for considering contributing to the Harmony project. This guide consolidates all the resources, tools, and tips you need to start contributing effectively. We value your input, no matter what skill set you have - whether you’re a developer, researcher, or data and AI enthusiast, or even if you’re in an entirely different field.
We recommend that you try the free web tool: Harmony App to understand how the tool works and what it does. Join our Discord Server, where you can interact with users and contributors, ask questions, and collaborate on ideas. Please also follow us on social media platforms: Twitter, LinkedIn, Facebook, YouTube.
We’ve split this guide into two sections, depending on whether you are intending to use Harmony in research or contribute to the code base:
There are two ways you can use Harmony in your work:
Some academic users start off on the web tool, and then switch to the Python or R library and work in Jupyter Notebooks or R Markdown to use the tool as part of their workflow.
pip install harmonydataimport harmonyinstall.packages("harmonydata") to install the packagelibrary(harmonydata)We have some example notebooks to help you get started with the Python and R libraries:
Here’s how you can help the project:
Harmony’s source code is all public and it’s under source control in Github, so we can see which changes were done to the project at any date in the past.
You are welcome to make your contributions to the library at any time. You can also come to our hackathons and other events and contribute in person.
We have four main repositories on Github under the harmonydata organisation:
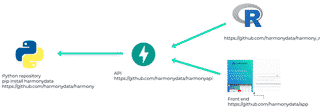
--recurse-submodules, e.g. git clone --recurse-submodules git@github.com:harmonydata/harmonyapi.gitYou can use Windows, Linux or Mac. We have made some videos to help you install Python and Harmony:
Here are the steps to get started:
If you just want to use the Python library without editing it, you can install it with pip install harmonydata. However, if you want to edit the source code, you will need to get it running from source.
git clone git@github.com:harmonydata/harmony.git. If you’re not familiar with Git and Github, we recommend you watch a tutorial on Git first (example video tutorial on Git)The API repository depends on the Python repository, which it contains as a submodule. So when you clone the API repository, please make sure to include --recurse-submodules:
git clone --recurse-submodules git@github.com:harmonydata/harmonyapi.git
The API builds as a Docker container, so in addition to the Python library’s dependencies, you will need to install FastAPI and Docker. There is a separate requirements.txt file for the API repository.
You can run the API with
python main.py
Clone the front end repository:
git clone git@github.com:harmonydata/app.git
Follow the instructions in the .env file to connect it to the Harmony API - you can connect either to the remote API, or to a local API.
For example, if you are already running the API locally, set .env and .env.development to:
REACT_APP_API_URL=http://localhost:8000
REACT_APP_API_EXAMPLES=$REACT_APP_API_URL/text/examples
REACT_APP_API_PARSE=$REACT_APP_API_URL/text/parse
REACT_APP_API_MATCH=$REACT_APP_API_URL/text/match
REACT_APP_API_VERSION=$REACT_APP_API_URL/info/version
REACT_APP_API_MODELS=$REACT_APP_API_URL/info/list-models
REACT_APP_ABSOLUTE_URL_PREFIX=http://localhost
Here is a video on how you can install and run both the back end and front end locally on your machine:
Clone the R repository:
git clone git@github.com:harmonydata/harmony_r.git
Harmony R connects to an API instance. By default it will connect to the remote API at https://api.harmonydata.ac.uk, but you can configure this with
harmonydata::set_url()
Each of the repositories has its own issue tracker. Before taking on an issue, please check that nobody is already working on it. Please write a comment at the bottom of an issue that you would like to pick up, so that other people don’t duplicate your work.
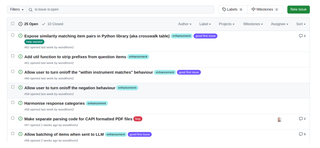
Above: This is a preview of the issues board. You can see that some issues are tagged “good first issue”. So they are good for new people to pick up.
You can also ask on Discord if you have any questions about how best to contribute.
It’s a good idea to check the open pull requests to check that nobody has already worked on that issue and submitted code back to the main project. For example, here are the pull requests for the Python library: https://github.com/harmonydata/harmony/pulls
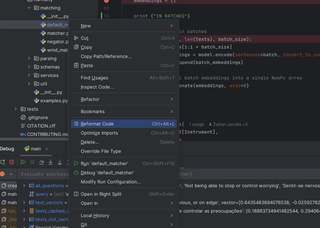
Harmony is mostly coded in Python. We use Pycharm IDE by JetBrains. Please ensure you are familiar with Python, HuggingFace, and FastAPI, or Javascript and React if you want to work on the front end.
See the example screenshot below of Pycharm’s formatter to format your code correctly:
tests and you can run them on your computer and Github actions will run them when you commit. They will tell you if you break any functionality.Harmony uses the pytest framework for testing. For more info on this, see the pytest documentation. To be interpreted and run, all test files and test functions need to be prefixed with test_.
The Harmony Python library https://github.com/harmonydata/harmony is the core Harmony functionality. Most of the logic is in this repo. This repo has unit tests which run automatically on commits to main.
However, the Harmony API repo https://github.com/harmonydata/harmonyapi uses the Harmony Python library as a submodule. When you update the Python library, please run the unit tests and integration tests in the API repo to check nothing is broken - including the Selenium tests which test the browser app end to end. You will need to install Selenium to run the tests.
Since the API repo includes the Python library as a submodule, when you update the Python library, you will need to update the submodule (in the harmonyapi repo, cd into the submodule folder and do git pull, then cd out and do git add, commit and push). We recommend you familiarise yourself with Git submodules.
Finally, the app repo https://github.com/harmonydata/app is the React front end. Please check you can run this repo locally also before you start contributing. To point the front end repo to a local copy of your API repo, please change the file .env to point to http://localhost:8000.
The preferred workflow for contributing to Harmony’s repository is to fork the repository that you’re working on, such as the Python library, on GitHub, clone, and develop on a new branch.
When you’re done, please run all unit tests and you can submit your changes back to the main project as a pull request. If you have worked on the core Python library, please also test your changes in the context of the Python API.
If you are able to fix an issue, please feel free to submit your code back to the project by making a pull request (PR) but if you don’t know how to do that, don’t worry! You can always send us your work on Discord or by email. Here’s a brief overview of the steps for making a pull request.
git clone git@github.com:harmonydata/harmony.git
cd harmony
git remote -v
git remote add upstream <https://github.com/harmonydata/harmony.git>
git remote -v
\> origin <https://github.com/<username>/Harmony.git> (fetch)
\> origin <https://github.com/<username>/Harmony.git> (push)
\> upstream <https://github.com/harmonydata/harmony.git> (fetch)
\> upstream <https://github.com/harmonydata/harmony.git> (push)
git fetch upstream
git checkout main
git merge upstream/main
git checkout main
git checkout -b <feature-branch>
Always use a feature branch. It’s good practice to never work on the main branch! Name the feature branch after your contribution.
git add <modified_files>;
git commitgit push --set-upstream origin my-feature-branchWe recommend to open a pull request early, so that other contributors become aware of your work and can give you feedback early on.
Please make your pull requests atomic. That is, please try to fix only one issue per pull request. If your pull request addresses three separate issues, it is very hard for moderators to merge it.
Please don’t make huge changes, such as adding many third party dependencies to requirements.txt, as this can quickly make the project bloated and we would ideally discuss alternatives before any more dependencies are added.
If you introduce a new feature, please can you document it, for example by making a script example in the script examples repository so that people will know how to use it.
Please write clear commit messages:
Fix bug in NLP model (#54). Github will detect the # in the message and automatically display your commit under the corresponding issue, which means that anyone can easily see that a particular issue has related commits, and vice versa.Sometimes we receive pull requests which modify 18 files and look like they’re rewriting the entire project. On looking through, often the contributor has accidentally committed files that were just part of their experimentation, or absolute paths within their computer. Or they rewrite a part of the project unrelated to what they’re working on.
It is very hard to review a pull request like this. With so many changes, we cannot easily identify if any changes have a side effect. In addition, if anyone else is working on a part of the project affected by your changes, it will be hard to resolve conflicts.
Please avoid using commands like git add * which adds all files in the directory - try to ensure that every file is added individually. You can always reach out to the Harmony team for a discussion.
If any of the above seems like magic to you, look up the Git documentation. If you get stuck, chat with us on Discord, or contact us at harmonydata.ac.uk.
When you first try running the code, you may encounter some errors. This is often because a 3rd party package such as Numpy, Pandas, Lxml or Huggingface has updated itself and broken a dependency somewhere. It’s a good idea to Google for the error and check if you can fix it with a simple change in version to the package that’s causing the issue.
After you have cloned the repository at https://github.com/harmonydata/harmonyapi, if the folder inside called harmony is empty, or at any point you get an error like the below, please check you have cloned with --recurse-submodules as below:
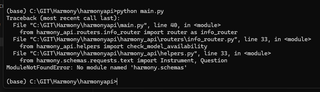
git clone --recurse-submodules https://github.com/harmonydata/harmonyapi.git
After you clone the front end, if you want the front end to communicate with your local copy of the API, you need to update .env and .env.development as described in the section on Working on Harmony front end.
If you see an error such as the below, check that your .env and .env.development are correct. You can also check if it runs connecting to the remote API.

You may be trying to run the Docker container locally so that you can run R and Harmony entirely on your computer without sending data over the internet.
Normally this command should run in command line / Terminal:
docker run -p 8000:80 harmonydata/harmonyapi
But if you get an error such as “manifest unknown” then that means that you need to supply the Docker image with an exact tag (which tells Docker which version of Harmony Docker to run). You can see all the Docker images here: https://hub.docker.com/r/harmonydata/harmonyapi/tags and you can pick the latest one and put it in the command, something like this:
docker run -p 8000:80 harmonydata/harmonyapi:20250311105945_1df2e89