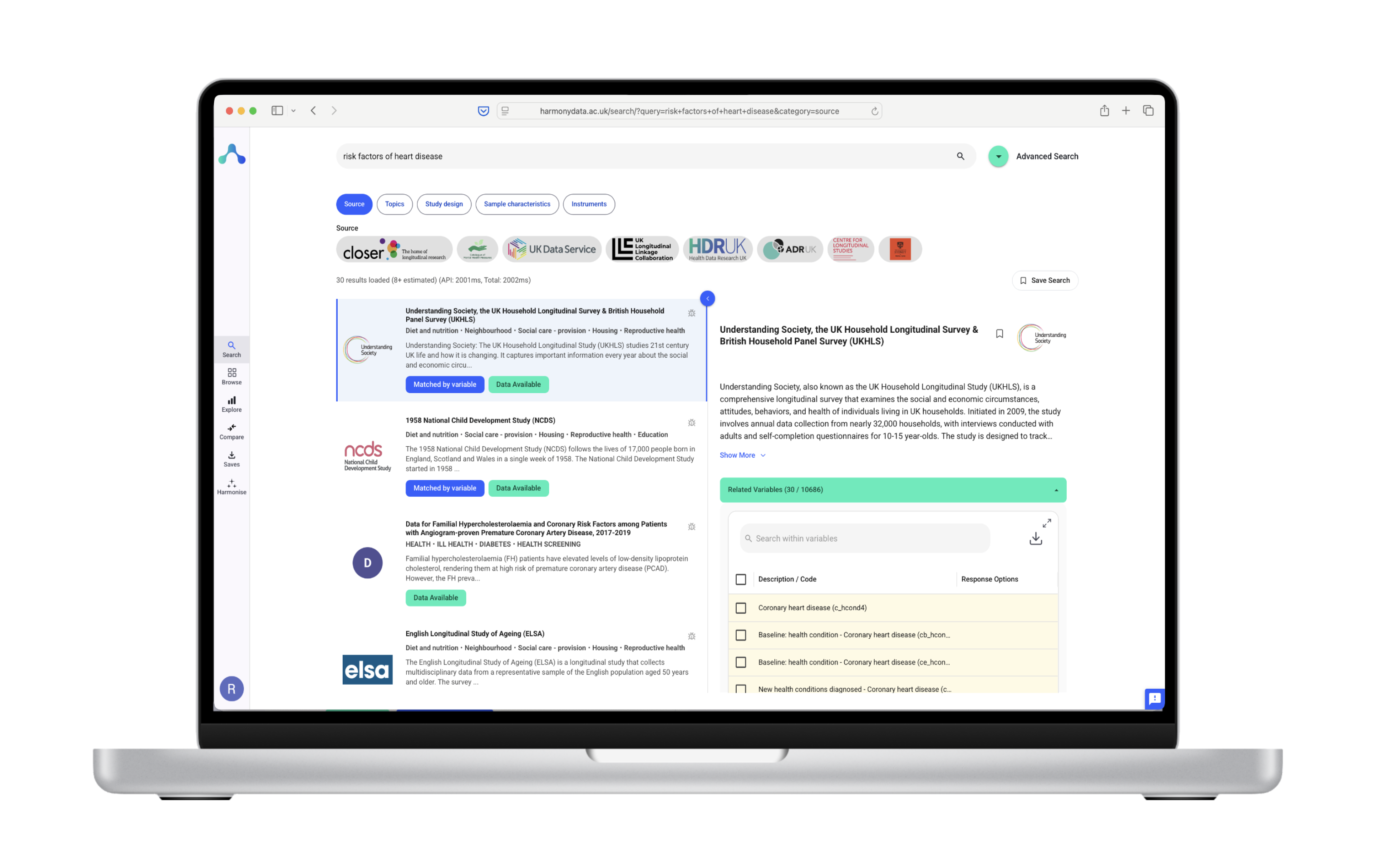
We have exposed functionality for external websites to integrate with Harmony and add an “import to Harmony” button, either generated in Javascript or in Python.
instrument_name and questions property in JSON - the questions must have a question_no and question_text properties eg:{
"instrument_name": "Smoking behaviour",
"questions": [
{
"question_no": "1",
"question_text": "Do you currently smoke or have you ever smoked?"
},
{
"question_no": "2",
"question_text": "[Do you currently use] nicotine replacement therapy?"
}
]
}
Encode it to URL safe base64 string - js-base64 is a good library for this.
Send it to the import URL - to maintain a single instance of the harmony tab / page the target must be set to the harmony URL
<a href="https://harmonydata.ac.uk/app/import/eyJpbnN0cnVtZW50X25hbWUiOiJUcmVhdG1lbnQgLSBtZWRpY2F0aW9uIiwicXVlc3Rpb25zIjpbeyJxdWVzdGlvbl9ubyI6IjEiLCJxdWVzdGlvbl90ZXh0IjoiSGF2ZSB5b3UgZXZlciB0YWtlbiBhbnRpLWRlcHJlc3NhbnRzPyJ9XX0" >Harmonise this scale with harmonydata.ac.uk</a>
from harmony import create_instrument_from_list, import_instrument_into_harmony_web
instrument = load_instrument_from_list(["Do you currently smoke or have you ever smoked?", "[Do you currently use] nicotine replacement therapy?"])
web_url = import_instrument_into_harmony_web(instrument)
print (web_url)
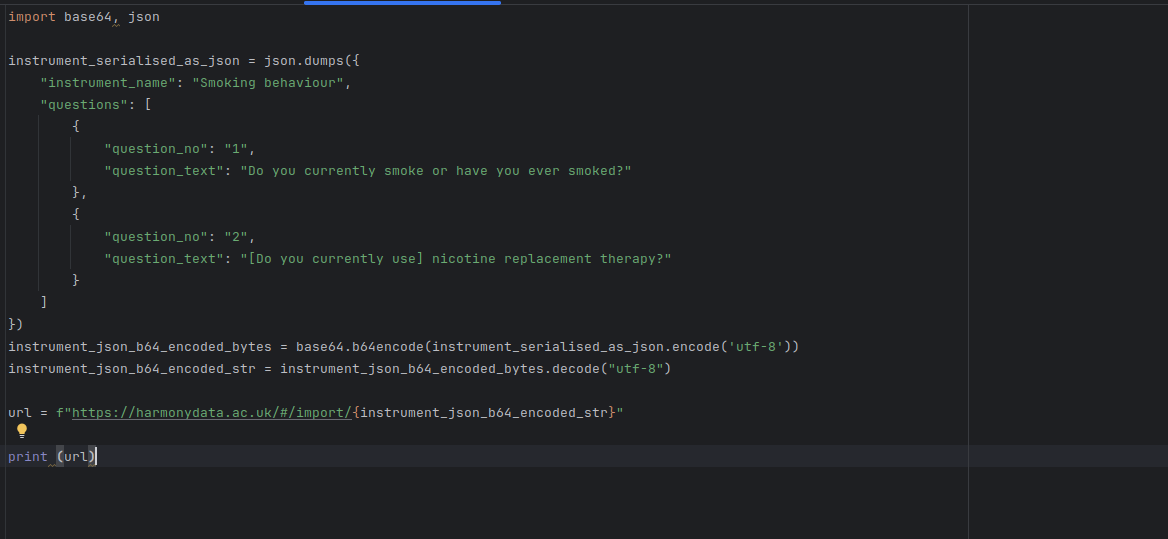
import base64, json
instrument_serialised_as_json = json.dumps({
"instrument_name": "Smoking behaviour",
"questions": [
{
"question_no": "1",
"question_text": "Do you currently smoke or have you ever smoked?"
},
{
"question_no": "2",
"question_text": "[Do you currently use] nicotine replacement therapy?"
}
]
})
instrument_json_b64_encoded_bytes = base64.urlsafe_b64encode(instrument_serialised_as_json.encode('utf-8'))
instrument_json_b64_encoded_str = instrument_json_b64_encoded_bytes.decode("utf-8")
url = f"https://harmonydata.ac.uk/app/#/import/{instrument_json_b64_encoded_str}"
print (url)
You can even import more than one instrument via the URL:
import base64, json
instrument_serialised_as_json = json.dumps([{
"instrument_name": "Smoking behaviour",
"questions": [
{
"question_no": "1",
"question_text": "Do you currently smoke or have you ever smoked?"
},
{
"question_no": "2",
"question_text": "[Do you currently use] nicotine replacement therapy?"
}
]
}, {
"instrument_name": "Smoking Review",
"questions": [
{
"question_no": "1",
"question_text": "Do you currently smoke?"
},
{
"question_no": "2",
"question_text": "Have you smoked in the past?"
}
]
}])
instrument_json_b64_encoded_bytes = base64.urlsafe_b64encode(instrument_serialised_as_json.encode('utf-8'))
instrument_json_b64_encoded_str = instrument_json_b64_encoded_bytes.decode("utf-8")
url = f"https://harmonydata.ac.uk/app/#/import/{instrument_json_b64_encoded_str}"
print (url)
this makes the following URL: