We are pleased to announce the publication of a paper validating Harmony on real-life data: Using natural language processing to facilitate the harmonisation of mental health questionnaires: a validation study using real-world data, authored by Eoin McElroy, Thomas Wood, Raymond Bond, Maurice Mulvenna, Mark Shevlin, George B. Ploubidis, Mauricio Scopel Hoffmann and Bettina Moltrecht, and published in BMC Psychiatry.
Our study aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of Natural Language Processing (NLP) in harmonising mental health questionnaires for cross-study research in areas such as mental health.
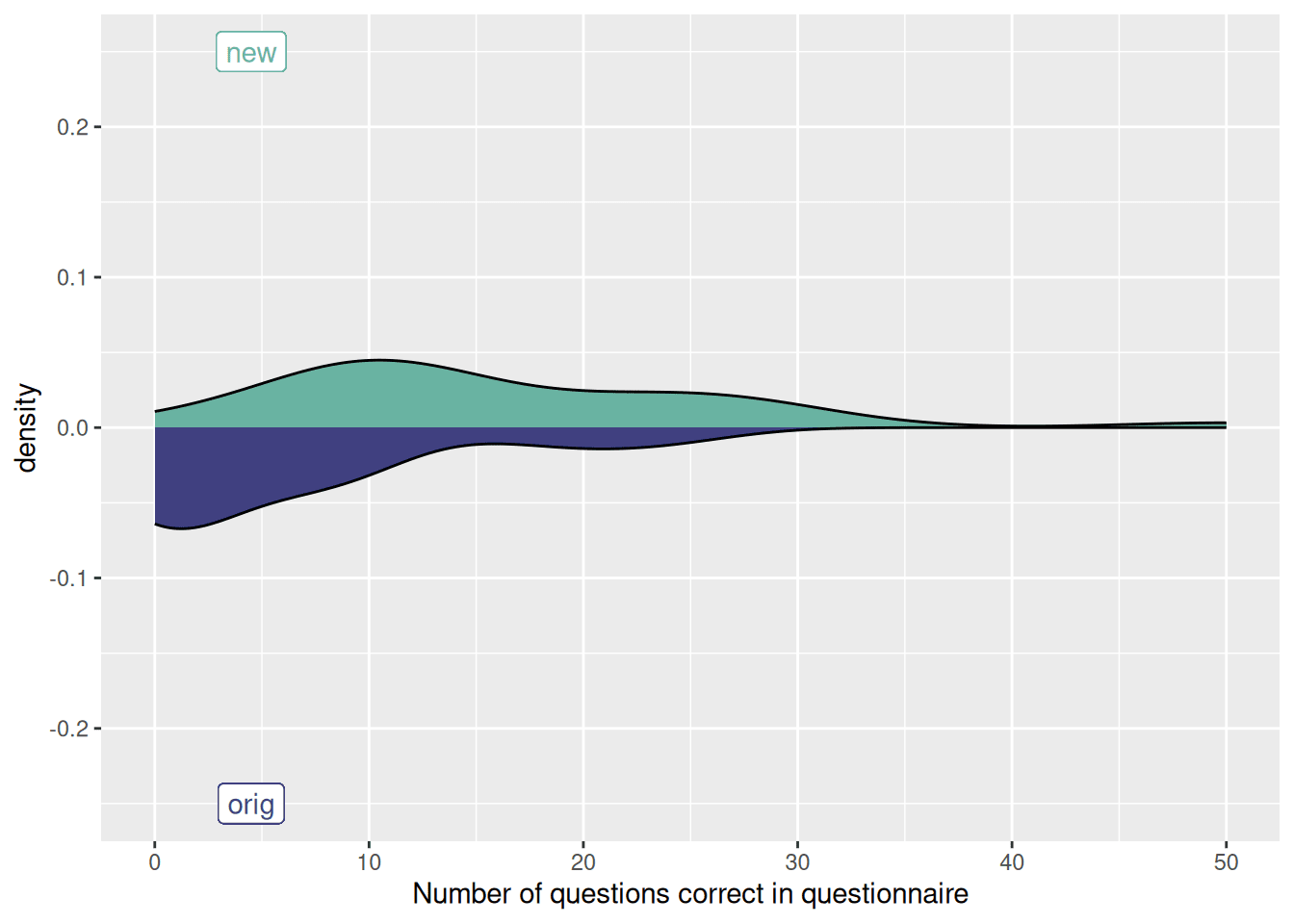
By comparing the semantic similarity of questionnaire items using NLP (the Sentence-BERT transformer model) with their actual correlation in a sample population, we found a moderate relationship (r = .48, p < .001) between the two measures. This suggests that NLP can accurately identify similar questions across different questionnaires.
While the NLP model showed promise in uncovering underlying patterns in the data, it required manual intervention to determine which relationships were truly relevant.
Our study showed that NLP can be a useful tool to match similar questions from different questionnaires, but it’s not perfect and should be used with caution.
A BibTeX entry for LaTeX users is
@article{mcelroy2024using,
title={Using natural language processing to facilitate the harmonisation of mental health questionnaires: a validation study using real-world data},
author={McElroy, Eoin and Wood, Thomas and Bond, Raymond and Mulvenna, Maurice and Shevlin, Mark and Ploubidis, George B and Hoffmann, Mauricio Scopel and Moltrecht, Bettina},
journal={BMC psychiatry},
volume={24},
number={1},
pages={530},
year={2024},
publisher={Springer}
}